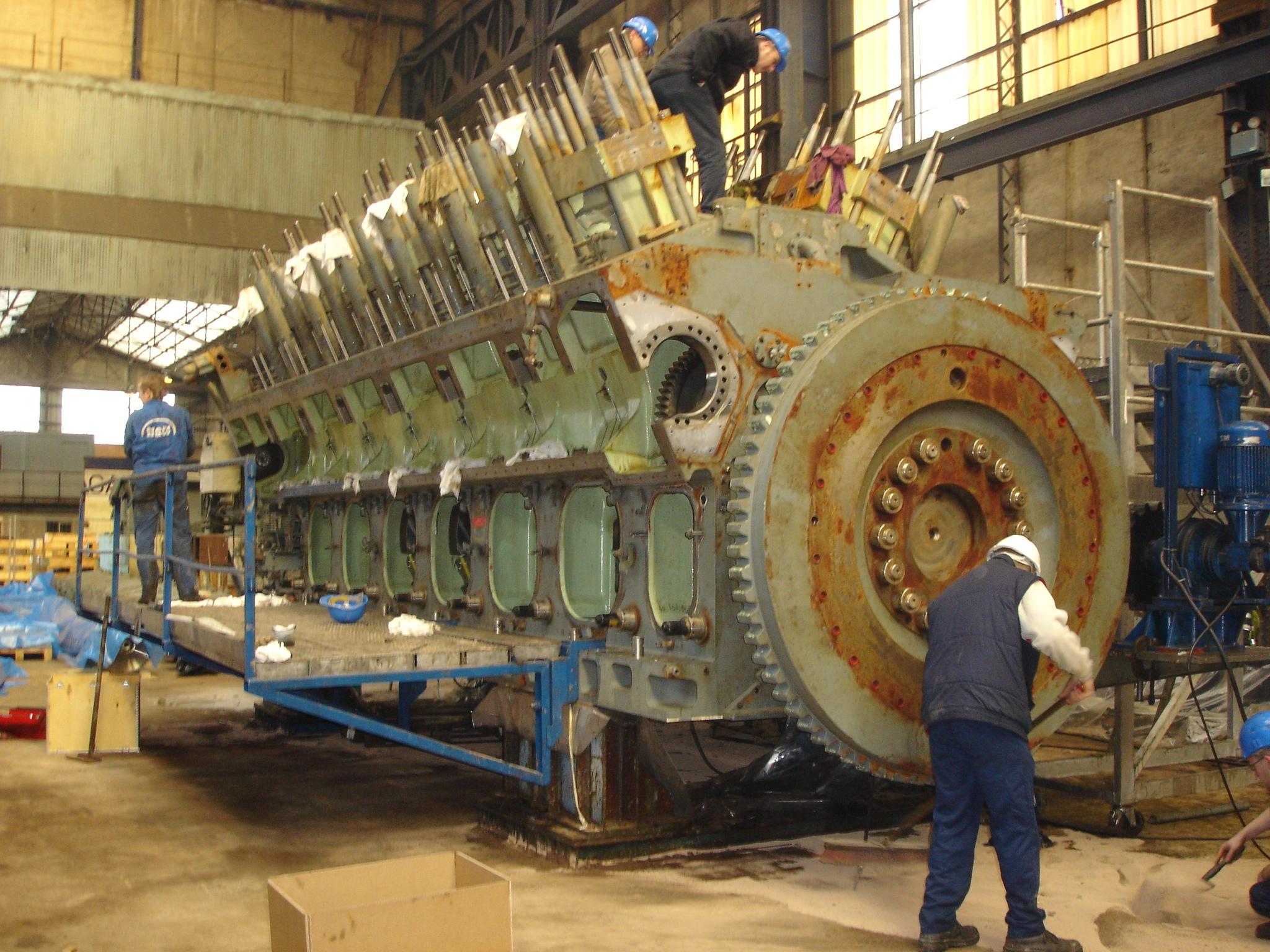
Marine engine life spans very according to the material they are burning and marine engine that run on gasoline require to be overhauled more frequently the marine diesel engines. On average a gasoline marine engine would require to be overhauled after approximately 1500 hours where as diesel engine would run an astonishing 5000 hours before they required overhauls? This is attributed to several factors that will be discussed in simple words.

The question concerning marine engine life spans expectancy differences is one that has many new marine vessel purchasers scratching their heads. There are several factors that contribute towards the fast overhaul requirement for marine gasoline engine compared to the diesel marine engines. First and foremost most gasoline engines are mounted on small or average size vessel that is desired to move relatively fast. This requirement for speed results in engine running at high revolutions or throttle as some would call it which wears the engine faster that an engine that was running at slows revolutions.
The faster the gasoline vessel moves over the water surface also contributes to the splashing of water, which eventually finds its way down in to the piston cylinder and increases the wearing process within the marine engine. The engines are also more exposed to the elements and come in to direct contact with water and dust while running greatly reducing their life expectancy compared to bigger water vessel that in most cases have the engines stationed well within the vessel securely in an engine room.
Diesel marine engines exhibited a triples lifetime mainly due to the speed they run at. They are designed to deliver tough power rather than high speed, a factor that contributes immensely towards the preservation of the diesel engines integrity. Marine engines also require liquid cooling which is pumped through the engine directly from the lake or sea and pumped right back out. This water could be potentially corrosive if the water is hard or saline. This corrosive water affects the piston sleeve outer lining which is considerable thinner on marine gasoline or petrol engines. Diesel engines tend to be manufactured with thicker sleeve materials due to the higher compression forces that are exerted within the engine.
Marine engine life spans thus depends of the way one was to use the engine, just like the way you come across automobile vehicles that have run for many years more than the expected engine lifespan requiring minimal repair to keep it running at peak condition. This same thing complies to marine engines and if a person cares for the engine carefully it would be able to surpass this hourly estimate, and in the same way if one was to use the engine roughly it would reduce it estimated lifespan by half of even less than that.
To get the longest Marine engine life spans they require proper maintenance and management to be able to perform over extended periods and while maintaining their structural integrity so that they can be overhauled or repaired to serve the used for another lengthy period a process that can be constantly repeated as long as the engine block or maintained and it structural integrity not compromised.
Marine Engine Life Spans,