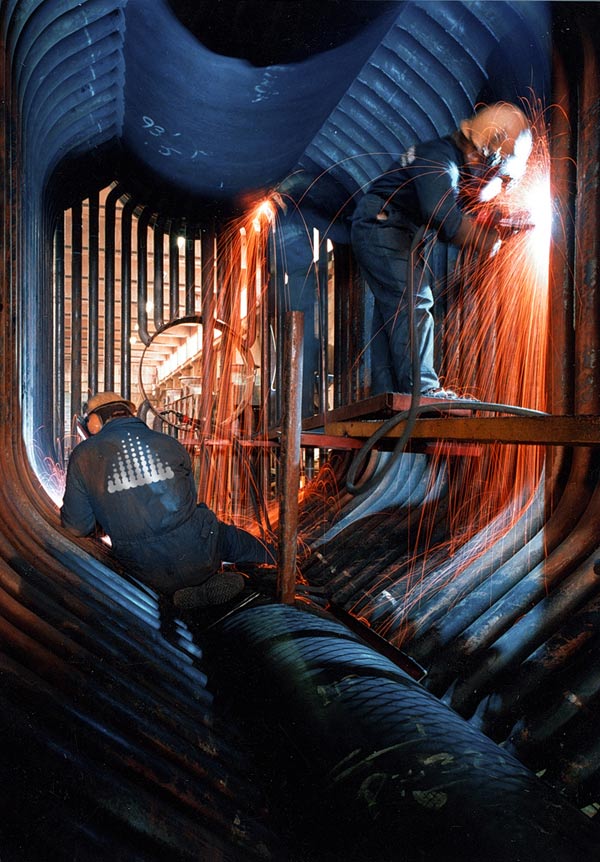
These days water tube boilers have nearly replaced the previously used smoke tube boilers on ships which have been shifted to auxiliary duties mostly. Let us find out about water tube boiler construction and see which all types of tubes are used in these boilers and what are their functions.
Generating Tubes:
As the name itself suggests, the generating tubes are the ones in which steam is generated through the evaporation of water. Obviously these tubes are placed along the path of flow of the hot gases and the phenomenon of heat exchange is that of convection.
The number and size of tubes are calculated carefully while planning the boiler construction since if the size of the tubes is too less, it would lead to overheating of the tubes due to excessive proportion of steam as compared to water.

The surface area available for heat exchange also has to be optimum because too large a surface area would mean that not only the steam would lose heat but would get cooled beyond the dew point thus leading to condensation which means water would get accumulated and would cause corrosion.
In modern versions of water tube boilers, the water walls are used for heat exchange instead of generating tubes, where the process of heat transfer is via radiation rather than convection.
Screen Tubes:
The purpose of the screen tubes in a water tube boiler is to shield the superheater tubes from excessive heating so that the heat radiated from the flames in the furnace do not damage them. Hence they are having a large size (diameter) which is necessary for keeping the temperatures low.
Water Wall Tubes:
The main purpose of these tubes is to keep the furnace heat controlled and reduce the use of refractory material in the same. Only in some types of boiler construction, these tubes also partly generate steam but despite of that their main aim is to act like a water wall and contain the furnace heat.
Downcomers:
These tubes mainly serve the purpose of supplying water to the water drum and headers. Downcomers are of large size and since their location lies outside the path of flow of the hot gases, they remain in a cool state all of the times.
Risers:
The top water wall headers in water tube boiler have a mixture of steam and water and this is returned to the steam drum via tubes known as risers.
Superheater Tubes:
Once water gets converted to steam, its temperature needs to be raised further to pump in more energy in the steam and this is done by imparting thermal energy to the steam in the form of superheat. This is done by heating it after the drum by the use of small size tubes which are placed along the path of flow of hot gases but after the screen tubes discussed above.
Care needs to be taken to protect these tubes from furnace heat radiation so as to prevent overheating. This is all the more important in this case since due to their smaller diameters they can get damaged especially since the specific heat of steam is not as large as the specific heat of water.
Superheater Support Tubes:
These are meant to provide water cooled support for superheater tubes and hence in order to fulfill their purpose they are made of large diameter.
In another article we would be dealing with the construction of these tubes like the materials used for different types of tubes, the maximum working temperature range calculated for each type of tubes and so forth.
References
Marine Boilers by Flanagan: Reed Elsevier Publications, UK